In the week between May 7th and 15th, 867 COVID-19 infections were found in Thailand Simmummuang fruit and vegetable market. Health investigators in Thailand identified the entrance of the public toilet as the suspected source of most infections. This rises our concern on the infection possibility of public toilets in Hong Kong.
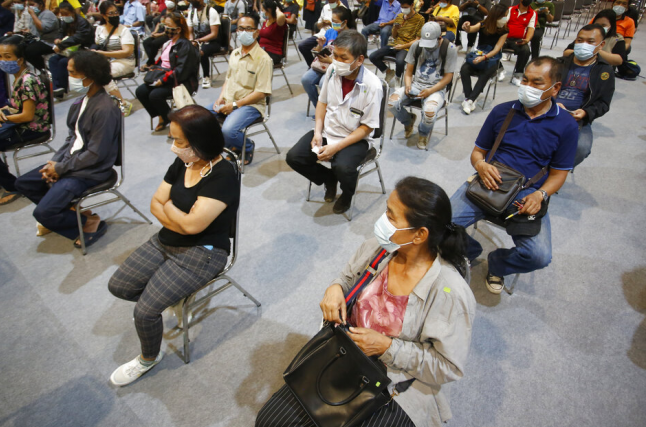


Simmummuang fruit and vegetable market: https://www.bastillepost.com/hongkong/article/8489819-%e6%b3%b0%e8%a1%97%e5%b8%82%e7%88%86867%e4%ba%ba%e6%96%b0%e5%86%a0%e7%a2%ba%e8%a8%ba-%e5%8e%9f%e5%85%87%e7%ab%9f%e6%98%af%e5%85%ac%e5%bb%81
Transmission Route in Public Toilets
According to Joseph Allen, associate professor at Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, public toilets can be an important source of COVID-19 spread. The major way of spread are flushing and touching.
When toilet water contains viruses and bacteria, the churning and bubbling of water creates particles that will float in the air. These viruses and bacteria will spread around the toilet, linger in the air and settle onto surfaces in the toilet. COVID-19 can survive in the air for 3 hours and even up to 24 hours in paper. Hence, the possible transmission route are people breathing in viruses when flushing and people touch installations in the toilets which viruses and bacteria settled.
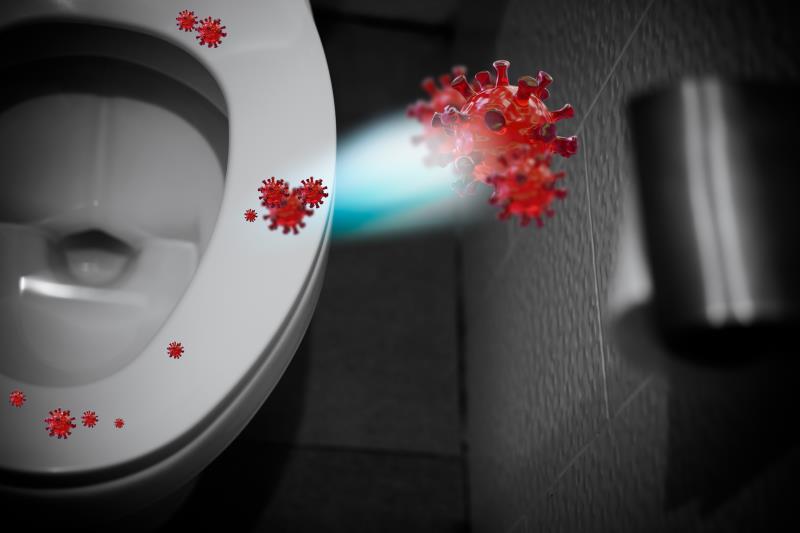

COVID-19 in toilets: https://specialty.mims.com/topic/covid-19-in-hospitals–toilets–staff–public-areas-show-contamination-
Ways to Prevent Infection in Public Toilets
In Hong Kong, the most common way to prevent infection in public toilets are wearing mask, wash hands after using the toilet and increase disinfecting arrangements. Nonetheless, these precautions still remain some loopholes in our dense against COVID-19. One common example is after washing hands, people still need to hold the door handle and open the door. If there are some viruses settled on the door handle before, the people will also get in touch with the viruses and may get infected if he or she then touch his or her mouth, nose or eyes. This example is just a tip of an iceberg, in public toilets, not only we need to touch door handles, but also push button toilet flush, faucet handle, soap dispenser handle, etc.. The more we touch, the higher the possibility that we are infected.

Touching doors in toilets: https://health.ucdavis.edu/coronavirus/covid-19-information/coronavirus-mistakes.html
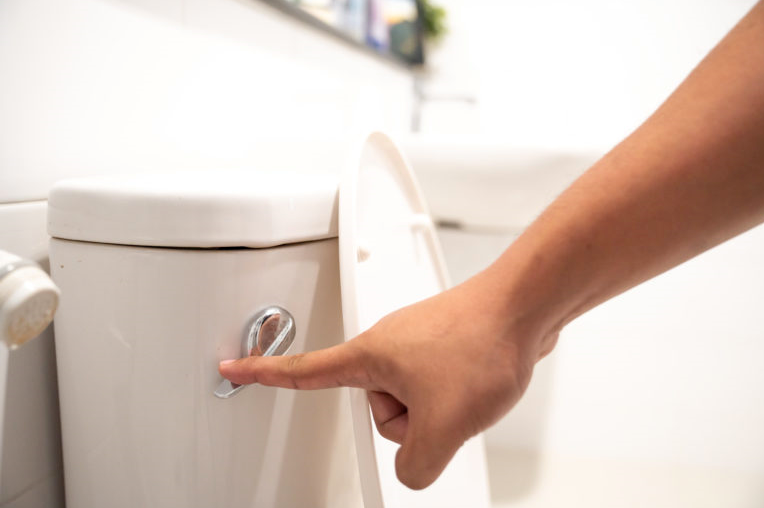

Touching Flush Button: https://www.pbs.org/newshour/health/public-bathrooms-carry-coronavirus-risks-heres-how-to-be-careful
To close up the loopholes, the best ways is to reduce the amount of viruses and bacteria spreading from flushing and minimize the need of touching in public toilets.
Reduce Viruses from Flushing
People no need to touch the toilet lid, the lid will automatically opens and closes when nearing or leaving the toilet. Therefore, even when people forget to close the toilet lid, the auto open/close lid will close the lid and reduce the amount of viruses and bacteria spreading.

Minimize the need for Touching
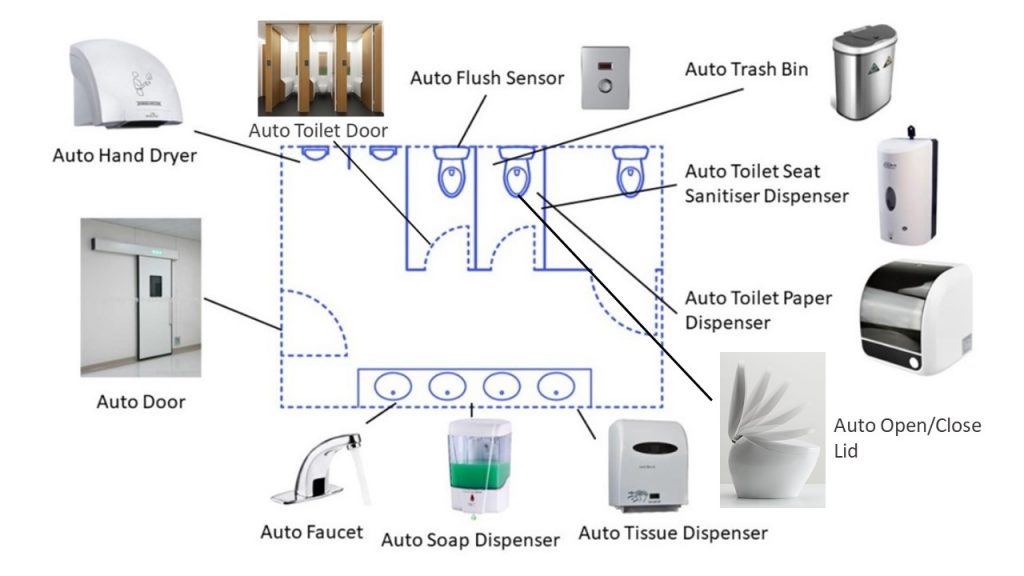
Although closing the toilet lid will reduce the amount of bacteria and viruses comes from flushing, there are still risk of getting infected in public toilets as it cannot minimize the amount of bacteria and viruses to 0. As a result, another effective precaution will be minimize the need for touching in public toilet, that is, to update a traditional toilet into a hand-free toilet. Here are the lists of installations in hand-free toilets.
- Auto Toilet Door
- Auto Flush Sensor
- Auto Trash Bin
- Auto Toilet Seat Sanitiser Dispenser
- Auto Toilet Paper Dispenser
- Auto Tissue Dispenser
- Auto Soap Dispenser
- Auto Faucet
- Auto Door
- Auto Hand Dryer
No ones knows when this pandemic will end, but we can try out best to minimize the possible spreading routes. Wearing mask and frequent disinfection are ways preventing viruses getting into our body, while upgrading toilets to hand-free toilets are smart ways to reduce the amount of bacteria exists in toilets. GBE will keep updating different measures to stop transmission route for the public to fight COVID-19.
GBE welcomes comments from professionals and enquiries from the Public



















 .
.







Recent Comments