Again , again and again, the water seepage investigation demands a highly complex analysis to both in-situ environment and desk study. The case presented here has been left unresolved over 2 years before GBE was called on board and finally took the issue to the end.
The annoying water dripping in middle of living area.
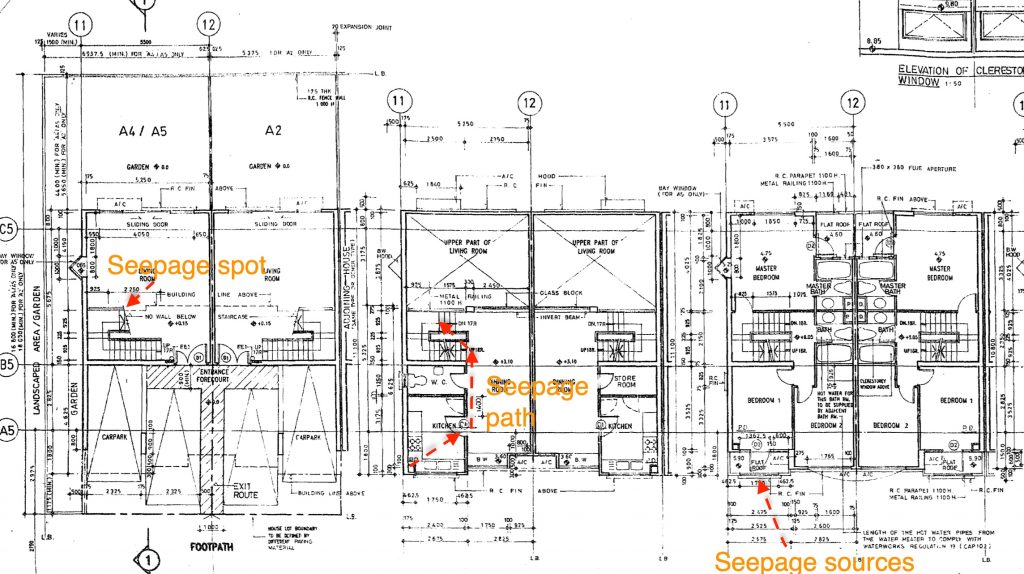
The building is a 4 storey house. It is generally deemed a luxury town house in Hong Kong. A water damp appeared on the ceiling of ground level where is the living area for family gathering. The damp worsened onward and started water dripping everytime the heavy rainfall happened. The seepage spot is about 8m away from the external wall. It became very misery where the water came.

Don’t undermine the importance of desk study
Having reviewed the layout plan, structural plan, decoration record photos and some maintenance history, we have considered a few possible sources which might be attributed to the water seepage. Following with the desk study, we took the site inspection firstly to verify the information obtained from desk study, to survey any other information which were not found in desk study. This really demanded a lot of professional call because those items outside the desk study were also very tricky.
Patient is important – Elimination Method with “Right” Testing
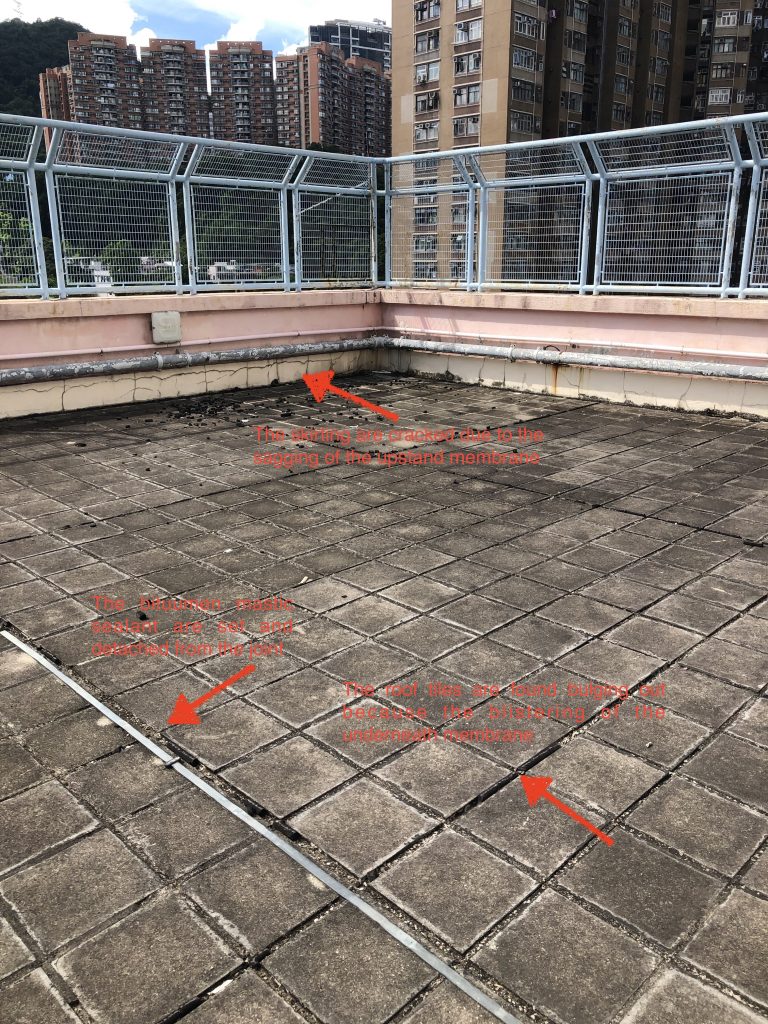
With reference to many literature , the way to identify the water seepage sources is “Elimination”. We have to establish the few possible sources and apply the “Right” testing to verify the assumption. This needs some experience together with the professional judgement. Sometimes , the site condition can render some cues for this judgement. In this case , we have done the survey to window , external wall, roof and some interior fitting out. The condition of window suggested its good and fair condition while the rain outlet at the roof and the skirting at the roof have found not properly done. We thus started the pooling test to the roof.
![]()
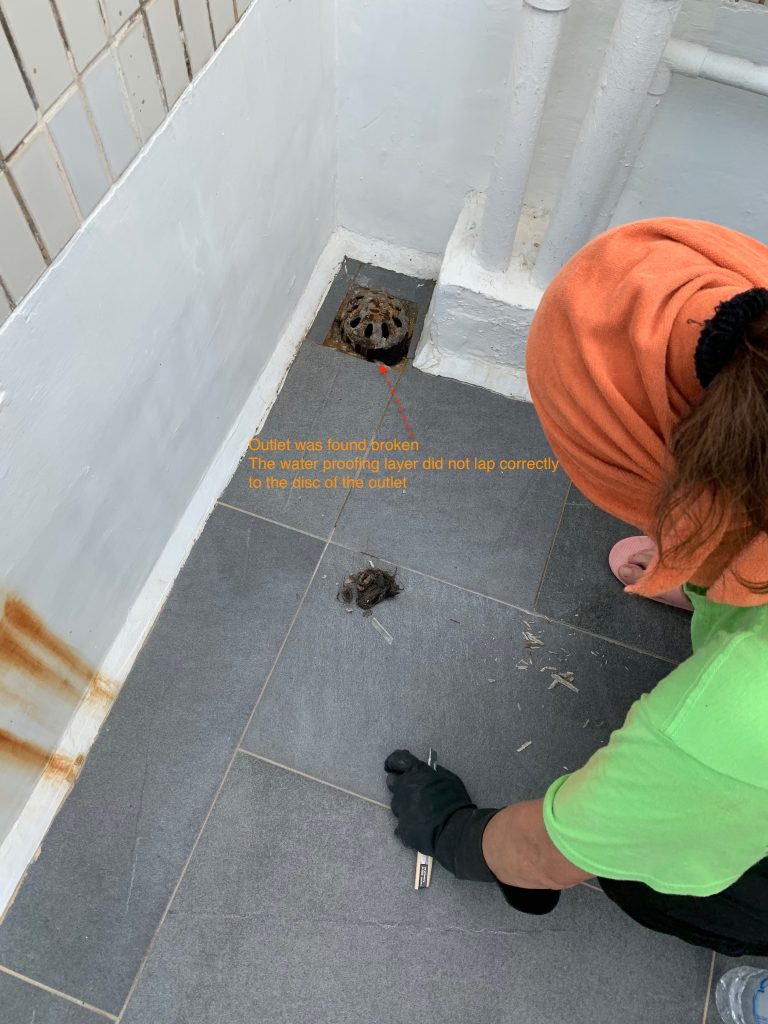

Judgement Call for the possible seepage path
With the aid of fluorescent liquid, the pool of liquid is prepared and stayed for 48 hours. Followed to this , we then applied the UV torch for tracing the “possible path” . Again, the “possible path” demanded a lot of imagination , but we found the cues in the record photos. We found that the conduit were laid in the recessed chase formed on the floor level. It could be pathway for water running.
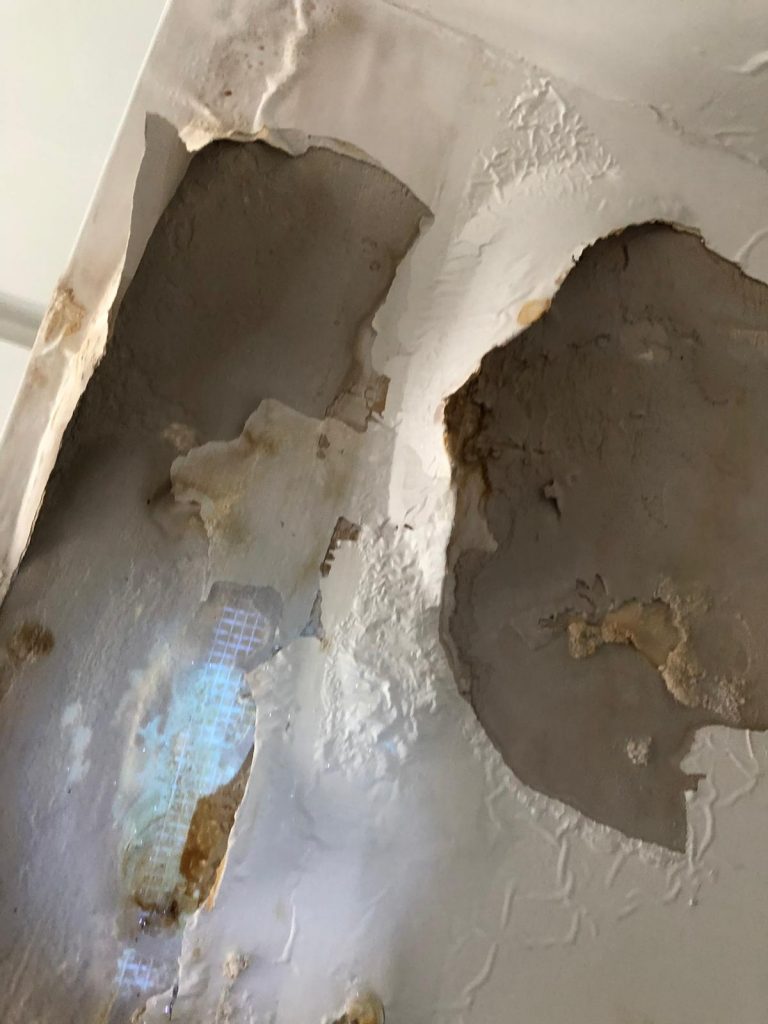 .
.

We found the seepage and fix it
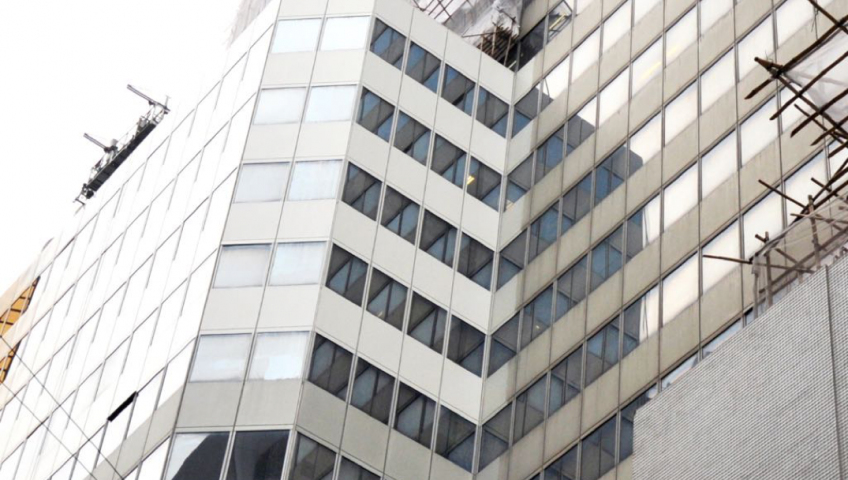
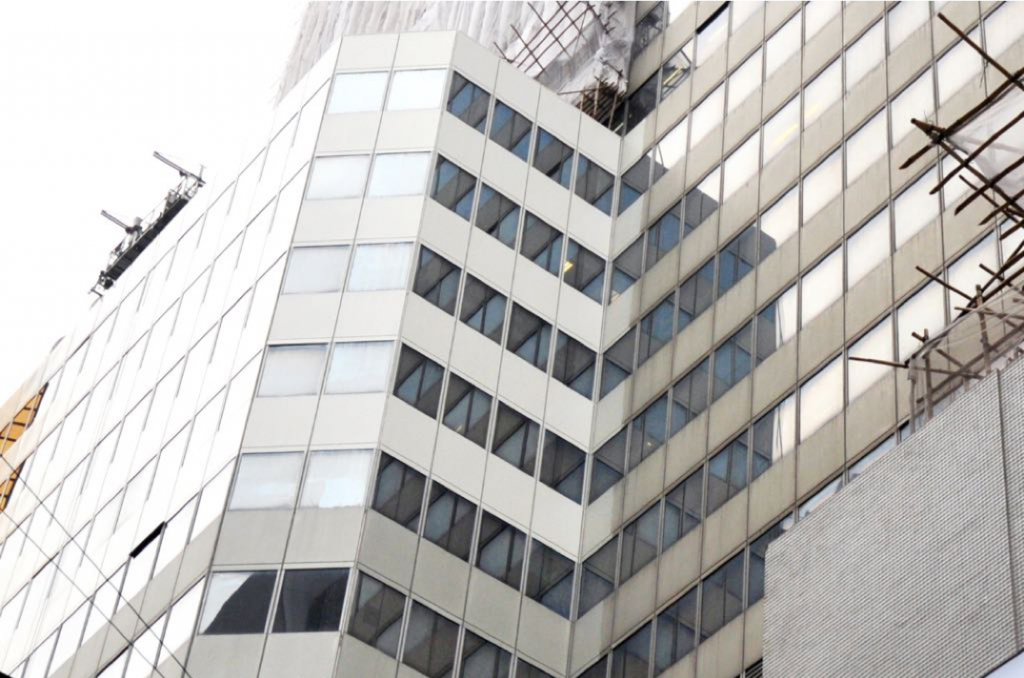
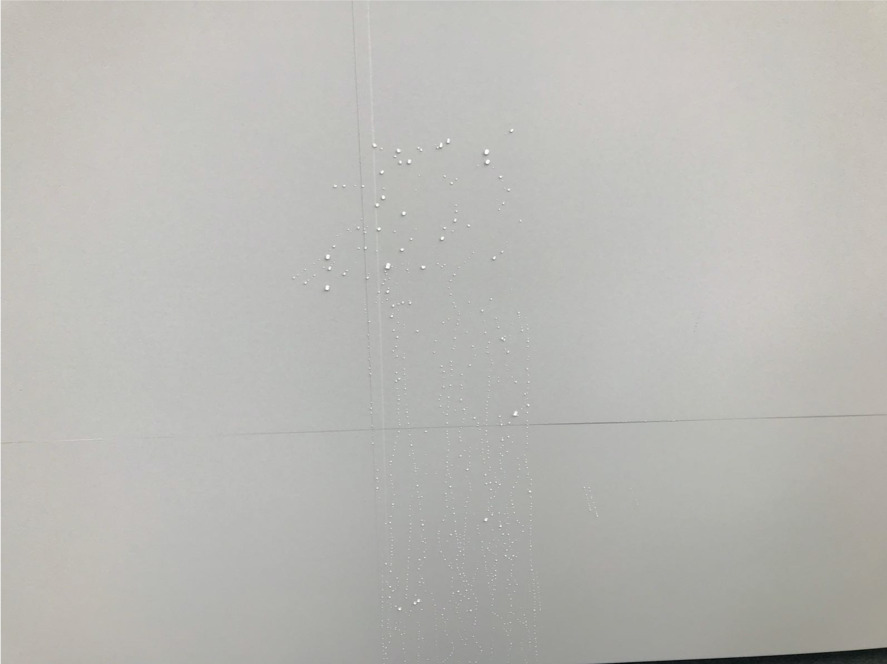
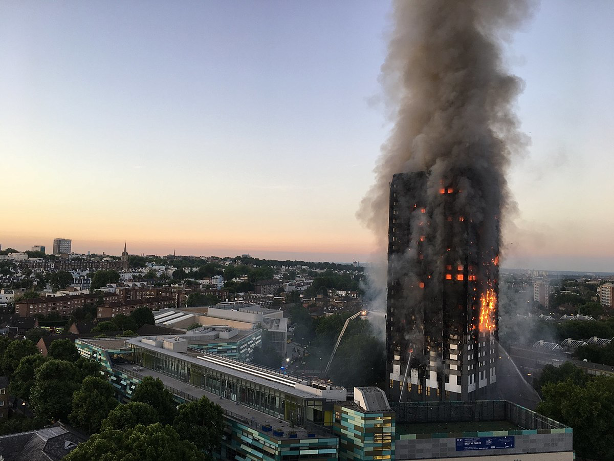
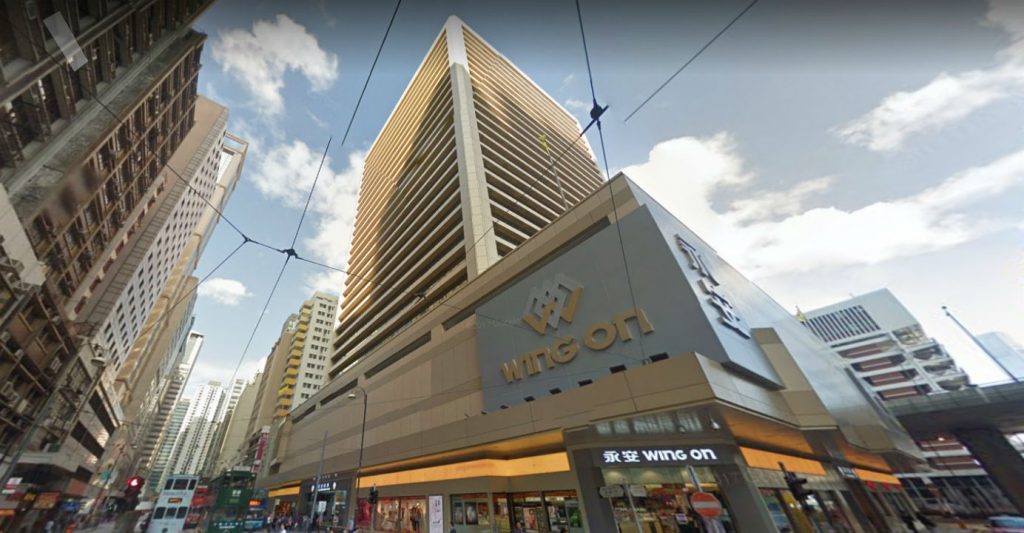
















 Photo : Wing On building in Sheung Wan was reported to have cladded with non-combustible cladding. Source from ejinsight on the pulse ( http://www.ejinsight.com)
Photo : Wing On building in Sheung Wan was reported to have cladded with non-combustible cladding. Source from ejinsight on the pulse ( http://www.ejinsight.com)







Recent Comments